Publications
-
Articles in scientific journals
-
Books
-
Theses
See also profiles on Publons,
Orcid or
Google Scholar.
1. Articles in scientific journals
 | Conformational Space of the Translocation Domain of Botulinum Toxin: Atomistic Modeling and Mesoscopic
Description of the Coiled-Coil Helix Bundle
Alexandre Delort, Grazia Cottone, Thérèse E. Malliavin, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstract
Int. J. Mol. Sci., 25: 2481, 2024.
 | Flexoelectric fluid membrane vesicles in spherical confinement
Niloufar Abtahi, Lila Bouzar, Nadia Saidi-Amroun, Martin Michael Müller |
EPL, 131(1): 18001, 2020. See also arXiv:2006.04475.
 | Isometric bending requires local constraints on free edges
Jemal Guven, Martin Michael Müller, Pablo Vázquez-Montejo |
Math. Mech. Solids, 24: 4051, 2019. See also arXiv:1904.05855.
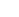
 | Helical Superstructure of Intermediate Filaments
Lila Bouzar, Martin Michael Müller, René Messina, Bernd Nöding, Sarah Köster, Hervé Mohrbach, Igor M. Kulić |
Intermediate filaments are the least explored among the large cytoskeletal elements.
We show here that they display conformational anomalies in narrow microfluidic channels.
Their unusual behavior can be understood as the consequence of a previously undetected, large scale
helically curved superstructure. Confinement in a channel orders the otherwise soft, strongly
fluctuating helical filaments and enhances their structural correlations, giving rise to experimentally
detectable, strongly oscillating tangent correlation functions. We propose an explanation for the detected
intrinsic curving phenomenon - an elastic shape instability that we call autocoiling. The mechanism
involves self-induced filament buckling via a surface stress located at the outside of the
cross-section. The results agree with ultrastructural findings and rationalize for the commonly observed
looped intermediate filament shapes. Beyond curvature, explaining the molecular origin of the detected helical
torsion remains an interesting challenge.
 Reduce
Read more Reduce
Read more
Phys. Rev. Lett., 122: 098101, 2019. See also arXiv:1803.04691.
 | Vesicle dynamics in confined steady and harmonically modulated Poiseuille flows
Zakaria Boujja, Chaouqi Misbah, Hamid Ez-Zahraouy, Abdelilah Benyoussef, Thomas John, Christian Wagner, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstract
Phys. Rev. E, 98: 043111, 2018. See also arXiv:1810.04500.
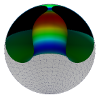 | Confining a fluid membrane vesicle of toroidal topology in an adhesive hard sphere
Lila Bouzar, Ferhat Menas, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstract
Read more
IOP Conf. Series: MSE, 186: 012021, 2017.
 | Squeezed helical elastica
Lila Bouzar, Martin Michael Müller, Pierre Gosselin, Igor M. Kulić, Hervé Mohrbach |
Abstract
Read more
Eur. Phys. J. E, 39: 114, 2016. See also arXiv:1606.03611.
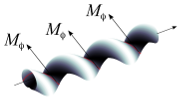 | How bio-filaments twist membranes
Julien Fierling, Albert Johner, Igor M. Kulić, Hervé Mohrbach, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstract
Soft Matter, 12: 5747, 2016.
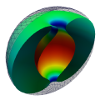 | Toroidal membrane vesicles in spherical confinement
Lila Bouzar, Ferhat Menas, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstract
Read more
Phys. Rev. E, 92: 032721, 2015. See also arXiv:1509.00765.
 | Non-linear buckling and symmetry breaking of a soft elastic sheet sliding on a cylindrical substrate
Norbert Stoop, Martin Michael Müller |
We consider the axial compression of a thin sheet wrapped around a rigid cylindrical substrate. In contrast to the wrinkling-to-fold transitions exhibited in similar systems, we find that the sheet always buckles into a single symmetric fold, while periodic solutions are unstable. Upon further compression, the solution breaks symmetry and stabilizes into a recumbent fold. Using linear analysis and numerics, we theoretically predict the buckling force and energy as a function of the compressive displacement. We compare our theory to experiments employing cylindrical neoprene sheets and find remarkably good agreement.
 Reduce
Read more Reduce
Read more
Int. J. Non-Linear Mech., 75: 115, 2015. See also arXiv:1503.05030.
 | Crunching Biofilament Rings
Julien Fierling, Martin Michael Müller, Hervé Mohrbach, Albert Johner, Igor M. Kulić |
Abstract
Read more
Europhys. Lett., 107(6): 68002, 2014. See also arXiv:1408.6787.
 | Confotronic dynamics of tubular filaments
Osman Kahraman, Hervé Mohrbach, Martin Michael Müller, Igor M. Kulić |
Abstract
Read more
Soft Matter, 10(16): pp. 2836-2847, 2014. See also arXiv:1312.3106.
 | Whirling skirts and rotating cones
Jemal Guven, J. A. Hanna, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstract
New J. Phys., 15: 113055, 2013. See also arXiv:1306.2619.
 | Myotubularin and PtdIns3P remodel the sarcoplasmic reticulum in muscle in vivo
Leonela Amoasii, Karim Hnia, Gaëtan Chicanne, Andreas Brech, Belinda Simone Cowling, Martin Michael Müller, Yannick Schwab, Pascale Koebel, Arnaud Ferry, Bernard Payrastre, Jocelyn Laporte |
Abstract
J. Cell Sci., 126(8): 1806, 2013.
 | Dipoles in thin sheets
Jemal Guven, J. A. Hanna, Osman Kahraman, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstract
Read more
Eur. Phys. J. E, 36: 106, 2013. See also arXiv:1212.3262.
 | Fluid membrane vesicles in confinement
Osman Kahraman, Norbert Stoop, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstract
Read more
New J. Phys., 14: 095021, 2012.
 | Petal shapes of sympetaleous flowers: the interplay between growth, geometry and elasticity
Martine Ben Amar, Martin Michael Müller, Miguel Trejo |
Abstract
Read more
New J. Phys., 14: 085014, 2012. Also featured in the Highlights of 2012.
 | Morphogenesis of membrane invaginations in spherical confinement
Osman Kahraman, Norbert Stoop, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstract
Read more
Europhys. Lett., 97(6): 68008, 2012. See also arXiv:1201.2518.
 | Conical instabilities on paper
Jemal Guven, Martin Michael Müller, Pablo Vázquez-Montejo |
Abstract
Read more
J. Phys. A: Math. Theor., 45(1): 015203, 2012. See also arXiv:1107.5008.
 | Interface-mediated interactions: Entropic forces of curved membranes
Pierre Gosselin, Hervé Mohrbach, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstract
Read more
Phys. Rev. E, 83(5): 051921, 2011. See also arXiv:1011.1221.
 | Self-Contact and Instabilities in the Anisotropic Growth of Elastic Membranes
Norbert Stoop, Falk K. Wittel, Martine Ben Amar, Martin Michael Müller, Hans J. Herrmann |
Abstract
Read more
Phys. Rev. Lett., 105(6): 068101, 2010. See also arXiv:1007.1871.
 | Cell Model Approach to Membrane Mediated Protein Interactions
Martin Michael Müller, Markus Deserno |
Abstract
Read more
Prog. Theor. Phys. Suppl., 184: pp. 351-363, 2010.
 | Hamiltonian formulation of surfaces with constant Gaussian curvature
Miguel Trejo, Martine Ben Amar, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstract
Read more
J. Phys. A: Math. Theor., 42(42): 425204, 2009.
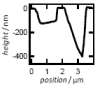 | Local Membrane Mechanics of Pore-Spanning Bilayers
Ingo Mey, Milena Stephan, Eva K. Schmitt, Martin Michael Müller, Martine Ben Amar, Claudia Steinem, Andreas Janshoff |
Abstract
Read more
J. Am. Chem. Soc., 131(20): pp. 7031-7039, 2009.
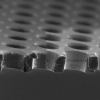 | Elasticity Mapping of Pore-Suspending Native Cell Membranes
Bärbel Lorenz, Ingo Mey, Siegfried Steltenkamp, Tamir Fine, Christina Rommel, Martin Michael Müller, Alexander Maiwald, Joachim Wegener, Claudia Steinem, Andreas Janshoff |
The mechanics of cellular membranes is governed by a non-equilibrium composite framework
consisting of the semiflexible filamentous cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix proteins linked to
the lipid bilayer. While elasticity information of plasma membranes has mainly been obtained from
whole cell analysis, techniques that allow to address local mechanical properties of cell
membranes are desirable to learn how their lipid and protein composition is reflected in the elastic
behavior on local length scales. Here, we introduce an approach based on basolateral
membranes of polar epithelial Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) II cells, prepared on a highly ordered porous substrate that
allows elastic mapping on a submicrometer length scale. A strong correlation between the
density of actin filaments and the measured membrane elasticity is found. Spatially resolved indentation experiments carried out with atomic force and fluorescence microscope permit to relate the supramolecular structure to the elasticity of cellular membranes. It is shown that the elastic response of the pore-spanning cell membranes is governed by the local bending modules rather than the lateral tension.
 Reduce
Read more Reduce
Read more
Small, 5(7): pp. 832-838, 2009.
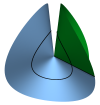 | Conical Defects in Growing Sheets
Martin Michael Müller, Martine Ben Amar, Jemal Guven |
Abstract
Read more
Phys. Rev. Lett., 101(15): 156104, 2008. See also arXiv:0807.1814.
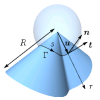 | How paper folds: bending with local constraints
Jemal Guven, Martin Michael Müller |
A variational framework is introduced to describe how a surface bends when it is subject to local constraints on its geometry. This framework is applied to describe the patterns of a folded sheet of paper. The unstretchability of paper implies a constraint on the surface metric; bending is penalized by an energy quadratic in mean curvature. The local Lagrange multipliers enforcing the constraint are identified with a conserved tangential stress that couples to the extrinsic curvature of the sheet. The framework is illustrated by examining the deformation of a flat sheet into a generalized cone.
 Reduce
Read more Reduce
Read more
J. Phys. A: Math. Theor., 41(5): 055203, 2008. See also arXiv:0712.0978.
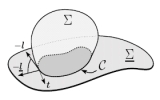 | Contact lines for fluid surface adhesion
Markus Deserno, Martin Michael Müller, Jemal Guven |
When a fluid surface adheres to a substrate, the location of the
contact line adjusts in order to minimize the overall energy. This
adhesion balance implies boundary conditions which depend on the
characteristic surface deformation energies. We develop a general
geometrical framework within which these conditions can be
systematically derived.
We treat both adhesion to a rigid substrate as well as adhesion
between two fluid surfaces, and illustrate our general results for
several important Hamiltonians involving both curvature and
curvature gradients. Some of these have previously been studied
using very different techniques, others are to our knowledge new.
What becomes clear in our approach is that, except for capillary
phenomena, these boundary conditions are not the manifestation
of a local force balance, even if the concept of surface stress is
properly generalized. Hamiltonians containing higher order surface
derivatives are not just sensitive to boundary translations but also
notice changes in slope or even curvature.
Both the necessity and the functional form of the corresponding
additional contributions follow readily from our treatment.
 Reduce
Read more Reduce
Read more
Phys. Rev. E, 76(1): 011605, 2007. See also cond-mat/0703019.
Also featured in the Virtual Journal of Biological Physics Research.
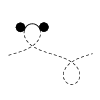 | Balancing torques in membrane-mediated interactions: Exact results and
numerical illustrations
Martin Michael Müller, Markus Deserno, Jemal Guven |
Torques on interfaces can be described by a divergence-free tensor
which is fully encoded in the geometry. This tensor consists of two
terms, one originating in the couple of the stress, the other capturing
an intrinsic contribution due to curvature. In analogy to the description
of forces in terms of a stress tensor, the torque on a particle can be
expressed as a line integral along any contour surrounding the particle.
Interactions between particles mediated by a fluid membrane are studied
within this framework. In particular, torque balance places a strong
constraint on the shape of the membrane. Symmetric two-particle
configurations admit simple analytical expressions which are valid
in the fully nonlinear regime; in particular, the problem may be
solved exactly in the case of two membrane-bound parallel cylinders.
This apparently simple system provides some flavor of the remarkably
subtle nonlinear behavior associated with membrane-mediated interactions.
 Reduce
Read more Reduce
Read more
Phys. Rev. E, 76(1): 011921, 2007. See also cond-mat/0702340.
Also featured in the Virtual Journal of Biological Physics Research.
 | Aggregation and vesiculation of membrane proteins by curvature-mediated
interactions
Benedict J. Reynwar, Gregoria Illya, Vagelis A. Harmandaris, Martin Michael Müller, Kurt Kremer, Markus Deserno |
Abstract
Read more
Nature 447(7143): pp. 461-464, 2007.
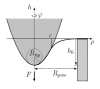 | How to determine local elastic properties of lipid bilayer membranes
from atomic-force-microscope measurements: A theoretical analysis
Davood Norouzi, Martin Michael Müller, Markus Deserno |
Measurements with an atomic force microscope (AFM) offer a direct way to
probe elastic properties of lipid bilayer membranes locally: provided
the underlying stress-strain relation is known, material parameters such as
surface tension or bending rigidity may be deduced.
In a recent experiment a pore-spanning membrane was poked with an AFM tip,
yielding a linear behavior of the force-indentation curves. A theoretical
model for this case is presented here which describes these curves in the
framework of Helfrich theory. The linear behavior of the measurements is
reproduced if one neglects the influence of adhesion between tip and membrane.
Including it via an adhesion balance changes the situation significantly:
force-distance curves cease to be linear, hysteresis and nonzero detachment
forces can show up. The characteristics of this rich scenario are discussed
in detail in this article.
 Reduce
Read more Reduce
Read more
Phys. Rev. E, 74(6): 061914, 2006. See also cond-mat/0602662.
Also featured in the Virtual Journal of Biological Physics Research.
 | Mechanical Properties of Pore-Spanning Lipid Bilayers Probed by Atomic Force Microscopy
Siegfried Steltenkamp, Martin Michael Müller, Markus Deserno, Christian Hennesthal, Claudia Steinem, Andreas Janshoff |
Abstract
Read more
Biophys. J., 91(1): pp. 217-226, 2006.
 | Interface mediated interactions between particles -- a geometrical approach
Martin Michael Müller, Markus Deserno, Jemal Guven |
Abstract
Read more
Phys. Rev. E, 72(6): 061407, 2005. See also cond-mat/0506019.
Also featured in the Virtual Journal of Biological Physics Research.
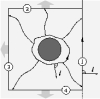 | Geometry of surface-mediated interactions
Martin Michael Müller, Markus Deserno, Jemal Guven |
Abstract
Read more
Europhys. Lett., 69(3): pp. 482-488, 2005. See also cond-mat/0409043.
2. Books
-
New Trends in the Physics and Mechanics of Biological Systems
Lecture Notes of the Les Houches Summer School, vol. 92 (Oxford University Press, 2011),
edited by Martine Ben Amar, Alain Goriely, Martin Michael Müller and Leticia Cugliandolo.
Chapter 9:
The physics of the cell membrane
Martin Michael Müller and Martine Ben Amar.
3. Theses
-
Theoretical examinations of interface mediated interactions between colloidal particles,
diploma thesis (2004).
-
Theoretical studies of fluid membrane mechanics, dissertation (2007).
-
Symmetry breaking in bioelasticity, habilitation thesis (2015).
|


