Publications
-
Articles in scientific journals
-
Books
-
Theses
See also profiles on Publons,
Orcid or
Google Scholar.
1. Articles in scientific journals
 | Conformational Space of the Translocation Domain of Botulinum Toxin: Atomistic Modeling and Mesoscopic
Description of the Coiled-Coil Helix Bundle
Alexandre Delort, Grazia Cottone, Thérèse E. Malliavin, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstract
Int. J. Mol. Sci., 25: 2481, 2024.
 | Flexoelectric fluid membrane vesicles in spherical confinement
Niloufar Abtahi, Lila Bouzar, Nadia Saidi-Amroun, Martin Michael Müller |
EPL, 131(1): 18001, 2020. See also arXiv:2006.04475.
 | Isometric bending requires local constraints on free edges
Jemal Guven, Martin Michael Müller, Pablo Vázquez-Montejo |
Math. Mech. Solids, 24: 4051, 2019. See also arXiv:1904.05855.
 | Helical Superstructure of Intermediate Filaments
Lila Bouzar, Martin Michael Müller, René Messina, Bernd Nöding, Sarah Köster, Hervé Mohrbach, Igor M. Kulić |
Abstract
Read more
Phys. Rev. Lett., 122: 098101, 2019. See also arXiv:1803.04691.
 | Vesicle dynamics in confined steady and harmonically modulated Poiseuille flows
Zakaria Boujja, Chaouqi Misbah, Hamid Ez-Zahraouy, Abdelilah Benyoussef, Thomas John, Christian Wagner, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstract
Phys. Rev. E, 98: 043111, 2018. See also arXiv:1810.04500.
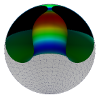 | Confining a fluid membrane vesicle of toroidal topology in an adhesive hard sphere
Lila Bouzar, Ferhat Menas, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstract
Read more
IOP Conf. Series: MSE, 186: 012021, 2017.
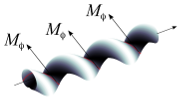
 | Squeezed helical elastica
Lila Bouzar, Martin Michael Müller, Pierre Gosselin, Igor M. Kulić, Hervé Mohrbach |
Abstract
Read more
Eur. Phys. J. E, 39: 114, 2016. See also arXiv:1606.03611.
 | How bio-filaments twist membranes
Julien Fierling, Albert Johner, Igor M. Kulić, Hervé Mohrbach, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstract
Soft Matter, 12: 5747, 2016.
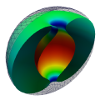 | Toroidal membrane vesicles in spherical confinement
Lila Bouzar, Ferhat Menas, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstract
Read more
Phys. Rev. E, 92: 032721, 2015. See also arXiv:1509.00765.
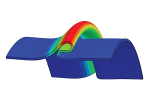 | Non-linear buckling and symmetry breaking of a soft elastic sheet sliding on a cylindrical substrate
Norbert Stoop, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstract
Read more
Int. J. Non-Linear Mech., 75: 115, 2015. See also arXiv:1503.05030.
 | Crunching Biofilament Rings
Julien Fierling, Martin Michael Müller, Hervé Mohrbach, Albert Johner, Igor M. Kulić |
Abstract
Read more
Europhys. Lett., 107(6): 68002, 2014. See also arXiv:1408.6787.
 | Confotronic dynamics of tubular filaments
Osman Kahraman, Hervé Mohrbach, Martin Michael Müller, Igor M. Kulić |
Abstract
Read more
Soft Matter, 10(16): pp. 2836-2847, 2014. See also arXiv:1312.3106.
 | Whirling skirts and rotating cones
Jemal Guven, J. A. Hanna, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstract
New J. Phys., 15: 113055, 2013. See also arXiv:1306.2619.
 | Myotubularin and PtdIns3P remodel the sarcoplasmic reticulum in muscle in vivo
Leonela Amoasii, Karim Hnia, Gaëtan Chicanne, Andreas Brech, Belinda Simone Cowling, Martin Michael Müller, Yannick Schwab, Pascale Koebel, Arnaud Ferry, Bernard Payrastre, Jocelyn Laporte |
The sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) is a specialized form of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) in skeletal muscle
and is essential for calcium homeostasis. The mechanisms involved in SR
remodeling and maintenance of SR subdomains are elusive. In this study, we identified
myotubularin (MTM1), a phosphatase mutated in X-linked centronuclear myopathy
(XLCNM), as a key regulator of phosphoinositide-3-monophosphate (PtdIns3P) levels at the
SR. Mtm1 deficient mouse muscles and myoblasts from XLCNM patients exhibit abnormal
SR/ER networks. In vivo modulation of MTM1 enzymatic activity in muscle using ectopic
expression of wild-type or a dead-phosphatase MTM1 protein leads to differential SR
remodeling. Active MTM1 is associated to flat membrane stacks, while dead-phosphatase
MTM1 mutant promotes highly curved cubic membranes originating from the SR and
enriched in PtdIns3P. Moreover, expression of the PtdIns3P binding module 2XFYVE also
modified the SR shape at triads. Our findings, supported by the parallel analysis of the Mtm1-
null mouse and in vivo study, reveal a direct function of MTM1 enzymatic activity in SR
remodeling and a key role for its substrate PtdIns3P in promoting SR membrane curvature in
skeletal muscle. We propose that alteration in SR remodeling is a primary cause of X-linked
centronuclear myopathy. The tight regulation of PtdIns3P on specific membrane subdomains
may be a general mechanism to control membrane curvature.
 Reduce Reduce
J. Cell Sci., 126(8): 1806, 2013.
 | Dipoles in thin sheets
Jemal Guven, J. A. Hanna, Osman Kahraman, Martin Michael Müller |
A flat elastic sheet may contain pointlike conical singularities that carry a metrical "charge" of Gaussian curvature. Adding such elementary defects to a sheet allows one to make many shapes, in a manner broadly
analogous to the familiar multipole construction in electrostatics. However, here the underlying field theory is non-linear,
and superposition of intrinsic defects is non-trivial as it must respect the immersion of the resulting surface in three
dimensions. We consider a "charge-neutral" dipole composed of two conical singularities of opposite sign.
Unlike the relatively simple electrostatic case, here there are two distinct stable minima and an infinity of unstable equilibria.
We determine the shapes of the minima and evaluate their energies in the thin-sheet regime where bending dominates
over stretching. Our predictions are in surprisingly good agreement with experiments on paper sheets.
 Reduce
Read more Reduce
Read more
Eur. Phys. J. E, 36: 106, 2013. See also arXiv:1212.3262.
 | Fluid membrane vesicles in confinement
Osman Kahraman, Norbert Stoop, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstract
Read more
New J. Phys., 14: 095021, 2012.
 | Petal shapes of sympetaleous flowers: the interplay between growth, geometry and elasticity
Martine Ben Amar, Martin Michael Müller, Miguel Trejo |
The growth of a thin elastic sheet imposes constraints on its geometry such as its Gaussian curvature KG.
In this paper, we construct the shapes of sympetalous bell-shaped flowers with a constant Gaussian curvature. Minimizing the bending energies
of both the petal and the veins, we are able to predict quantitatively the global shape of these flowers. We discuss two toy problems
where the Gaussian curvature is either negative or positive. In the former case the axisymmetric pseudosphere turns out to mimic the correct
shape before edge curling; in the latter case, singularities of the mathematical surface coincide with strong veins. Using a variational
minimization of the elastic energy, we find that the optimal number for the veins is either four, five or six, a number which is deceptively
close to the statistics on real flowers in nature.
 Reduce
Read more Reduce
Read more
New J. Phys., 14: 085014, 2012. Also featured in the Highlights of 2012.
 | Morphogenesis of membrane invaginations in spherical confinement
Osman Kahraman, Norbert Stoop, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstract
Read more
Europhys. Lett., 97(6): 68008, 2012. See also arXiv:1201.2518.
 | Conical instabilities on paper
Jemal Guven, Martin Michael Müller, Pablo Vázquez-Montejo |
Abstract
Read more
J. Phys. A: Math. Theor., 45(1): 015203, 2012. See also arXiv:1107.5008.
 | Interface-mediated interactions: Entropic forces of curved membranes
Pierre Gosselin, Hervé Mohrbach, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstract
Read more
Phys. Rev. E, 83(5): 051921, 2011. See also arXiv:1011.1221.
 | Self-Contact and Instabilities in the Anisotropic Growth of Elastic Membranes
Norbert Stoop, Falk K. Wittel, Martine Ben Amar, Martin Michael Müller, Hans J. Herrmann |
We investigate the morphology of thin discs and rings growing in circumferential direction. Recent analytical results suggest that this growth produces symmetric excess cones (e-cones). We study the stability of such solutions considering self-contact and bending stress. We show that, contrary to what was assumed in previous analytical solutions, beyond a critical growth factor, no symmetric e-cone solution is energetically minimal any more. Instead, we obtain skewed e-cone solutions having lower energy, characterized by a skewness angle and repetitive spiral winding with increasing growth. These results are generalized to discs with varying thickness and rings with holes of different radii.
 Reduce
Read more Reduce
Read more
Phys. Rev. Lett., 105(6): 068101, 2010. See also arXiv:1007.1871.
 | Cell Model Approach to Membrane Mediated Protein Interactions
Martin Michael Müller, Markus Deserno |
Abstract
Read more
Prog. Theor. Phys. Suppl., 184: pp. 351-363, 2010.
 | Hamiltonian formulation of surfaces with constant Gaussian curvature
Miguel Trejo, Martine Ben Amar, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstract
Read more
J. Phys. A: Math. Theor., 42(42): 425204, 2009.
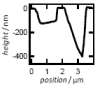 | Local Membrane Mechanics of Pore-Spanning Bilayers
Ingo Mey, Milena Stephan, Eva K. Schmitt, Martin Michael Müller, Martine Ben Amar, Claudia Steinem, Andreas Janshoff |
Abstract
Read more
J. Am. Chem. Soc., 131(20): pp. 7031-7039, 2009.
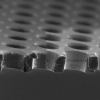 | Elasticity Mapping of Pore-Suspending Native Cell Membranes
Bärbel Lorenz, Ingo Mey, Siegfried Steltenkamp, Tamir Fine, Christina Rommel, Martin Michael Müller, Alexander Maiwald, Joachim Wegener, Claudia Steinem, Andreas Janshoff |
Abstract
Read more
Small, 5(7): pp. 832-838, 2009.
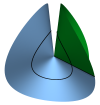 | Conical Defects in Growing Sheets
Martin Michael Müller, Martine Ben Amar, Jemal Guven |
A growing or shrinking disc will adopt a conical shape, its intrinsic geometry characterized by a surplus angle φe at the apex. If growth is slow, the cone will find its equilibrium. Whereas this is trivial if φe≤0, the disc can fold into one of a discrete infinite number of states if φe is positive. We construct these states in the regime where bending dominates, determine their energies and how stress is distributed in them. For each state a critical value of φe is identified beyond which the cone touches itself. Before this occurs, all states are stable; the ground state has twofold symmetry.
 Reduce
Read more Reduce
Read more
Phys. Rev. Lett., 101(15): 156104, 2008. See also arXiv:0807.1814.
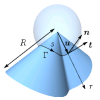 | How paper folds: bending with local constraints
Jemal Guven, Martin Michael Müller |
Abstract
Read more
J. Phys. A: Math. Theor., 41(5): 055203, 2008. See also arXiv:0712.0978.
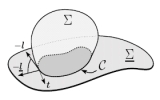 | Contact lines for fluid surface adhesion
Markus Deserno, Martin Michael Müller, Jemal Guven |
When a fluid surface adheres to a substrate, the location of the
contact line adjusts in order to minimize the overall energy. This
adhesion balance implies boundary conditions which depend on the
characteristic surface deformation energies. We develop a general
geometrical framework within which these conditions can be
systematically derived.
We treat both adhesion to a rigid substrate as well as adhesion
between two fluid surfaces, and illustrate our general results for
several important Hamiltonians involving both curvature and
curvature gradients. Some of these have previously been studied
using very different techniques, others are to our knowledge new.
What becomes clear in our approach is that, except for capillary
phenomena, these boundary conditions are not the manifestation
of a local force balance, even if the concept of surface stress is
properly generalized. Hamiltonians containing higher order surface
derivatives are not just sensitive to boundary translations but also
notice changes in slope or even curvature.
Both the necessity and the functional form of the corresponding
additional contributions follow readily from our treatment.
 Reduce
Read more Reduce
Read more
Phys. Rev. E, 76(1): 011605, 2007. See also cond-mat/0703019.
Also featured in the Virtual Journal of Biological Physics Research.
 | Balancing torques in membrane-mediated interactions: Exact results and
numerical illustrations
Martin Michael Müller, Markus Deserno, Jemal Guven |
Abstract
Read more
Phys. Rev. E, 76(1): 011921, 2007. See also cond-mat/0702340.
Also featured in the Virtual Journal of Biological Physics Research.
 | Aggregation and vesiculation of membrane proteins by curvature-mediated
interactions
Benedict J. Reynwar, Gregoria Illya, Vagelis A. Harmandaris, Martin Michael Müller, Kurt Kremer, Markus Deserno |
Abstract
Read more
Nature 447(7143): pp. 461-464, 2007.
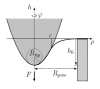 | How to determine local elastic properties of lipid bilayer membranes
from atomic-force-microscope measurements: A theoretical analysis
Davood Norouzi, Martin Michael Müller, Markus Deserno |
Abstract
Read more
Phys. Rev. E, 74(6): 061914, 2006. See also cond-mat/0602662.
Also featured in the Virtual Journal of Biological Physics Research.
 | Mechanical Properties of Pore-Spanning Lipid Bilayers Probed by Atomic Force Microscopy
Siegfried Steltenkamp, Martin Michael Müller, Markus Deserno, Christian Hennesthal, Claudia Steinem, Andreas Janshoff |
Abstract
Read more
Biophys. J., 91(1): pp. 217-226, 2006.
 | Interface mediated interactions between particles -- a geometrical approach
Martin Michael Müller, Markus Deserno, Jemal Guven |
Particles bound to an interface interact because they deform its shape.
The stresses that result are fully encoded in the geometry and described
by a divergence-free surface stress tensor. This stress tensor can be
used to express the force on a particle as a line integral along any
conveniently chosen closed contour that surrounds the particle. The
resulting expression is exact (i.e., free of any 'smallness' assumptions)
and independent of the chosen surface parametrization. Additional surface
degrees of freedom, such as vector fields describing lipid tilt, are readily
included in this formalism. As an illustration, we derive the exact force
for several important surface Hamiltonians in various symmetric two-particle
configurations in terms of the midplane geometry; its sign is evident in
certain interesting limits. Specializing to the linear regime, where the
shape can be analytically determined, these general expressions yield
force-distance relations, several of which have originally been derived
by using an energy based approach.
 Reduce
Read more Reduce
Read more
Phys. Rev. E, 72(6): 061407, 2005. See also cond-mat/0506019.
Also featured in the Virtual Journal of Biological Physics Research.
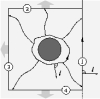 | Geometry of surface-mediated interactions
Martin Michael Müller, Markus Deserno, Jemal Guven |
Abstract
Read more
Europhys. Lett., 69(3): pp. 482-488, 2005. See also cond-mat/0409043.
2. Books
-
New Trends in the Physics and Mechanics of Biological Systems
Lecture Notes of the Les Houches Summer School, vol. 92 (Oxford University Press, 2011),
edited by Martine Ben Amar, Alain Goriely, Martin Michael Müller and Leticia Cugliandolo.
Chapter 9:
The physics of the cell membrane
Martin Michael Müller and Martine Ben Amar.
3. Theses
-
Theoretical examinations of interface mediated interactions between colloidal particles,
diploma thesis (2004).
-
Theoretical studies of fluid membrane mechanics, dissertation (2007).
-
Symmetry breaking in bioelasticity, habilitation thesis (2015).
|


